Scene objects
PixelOver uses a parent–child object hierarchy, meaning that an object’s transformation (position, rotation, scale, etc.) is evaluated relative to its parent.
Canvas
The Canvas is always the top-most item in the scene tree. It represents the page on which all objects are displayed.
The Canvas exposes two main properties:
-
Canvas Transform
Size defines the page size. It corresponds to the rectangle filled with a checkered background. -
Exported Area
This area determines what will be exported.
When it is not set to auto and the Canvas is selected, it appears as a modifiable blue rectangle.
The Canvas only accepts layers as children.
Layer
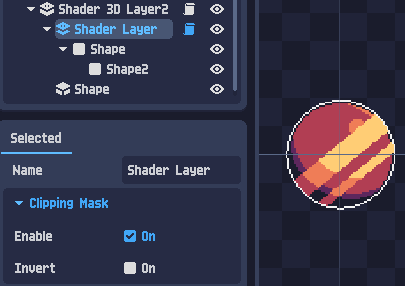
Layers are used to organize objects and separate rendering logic. A layer can have shader effects, indicated by the icon:
When the shader icon is blue, the layer’s shader is selected and its properties are displayed in the Shader panel.
A layer can also act as a clipping mask for another layer.
To enable this, activate clipping mask mode and select the target layer, or drag and drop one layer into another.
2D Layer
A 2D Layer only accepts 2D objects as children.
3D Layer
A 3D Layer includes camera-related properties such as projection type and rotation.
Several presets are available, and all settings can be customized. The layer also provides environment and sunlight controls.
A 3D Layer only accepts 3D objects as children.
Objects
Visual objects have a visibility property and can be shown or hidden. Objects can also have separate shader effects.
Most visual objects can also emit particles, including images, animated images, shapes, and 3D models.
2D Objects
A 2D Object uses 2D transform properties: position, rotation, scale, and skew.
Shape
A Shape is a basic rectangle.
Corners can be rounded to create rounded rectangles or perfect circles.
Image
An Image is an object that displays an image resource.
Resampling filters are applied when the image is transformed (scaled, rotated, or skewed).
Animated Image
An Animated Image behaves like a standard Image but uses an animated image resource. A Frame input is available to change the currently displayed frame.
Gradient
A Gradient can be used to fill shapes, images, or to define line colors in shaders.
Bone
A Bone provides a specialized transform tool designed for animation workflows.
Bones can also use transformation constraints such as
Inverse Kinematics.
3D Objects
A 3D Object uses 3D transform properties: position, rotation, and scale.
3D Container
A 3D Container is an empty 3D object used to group and transform its children together, making complex hierarchies easier to manage.
3D Shape
A 3D Shape can be set to different basic shapes such as a cube, sphere, or cylinder.
A material can be assigned to a 3D Shape. Without a material, only the base color can be modified.
3D Model
A 3D Model is created from a mesh resource.
3D Scene
A 3D Scene contains one or more 3D models. Models may be rigged and include animations.
A scene is handled as a single object, which makes it easier to keep content synchronized when it is modified externally.
You can also edit 3D model bone poses and apply Inverse Kinematics to them.
3D Bone
A 3D Bone is similar to a 2D Bone but operates in 3D space.
It uses a standard 3D gizmo for manipulation and also supports camera-aligned rotation when the bone is grabbed directly.